
MCP Servers with Code Mode: The missing piece in Agentic AI
A practical look at why MCP tool calling hits scaling limits, and how Code Mode (typed APIs + sandboxed execution) unlocks efficient multi-step agent workflows.
Aug 14, 2025
10 min read

Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) helps AI systems answer with better facts. The model first retrieves relevant passages from your knowledge base. It then uses that context to generate a response. This keeps answers current, grounded, and easier to verify.
This guide explains how to build a production RAG system step by step. We cover architecture, document parsing, retrieval quality, response quality, and evaluation. The same framework works for internal assistants, PDF workflows, and customer support bots.
RAG follows a simple flow: retrieve, then generate. Because the model sees trusted context before it answers, hallucinations drop and factual consistency improves. In short, RAG helps the model rely on your documents instead of memory alone.
Why it matters:
Common use cases:

Users upload PDFs and instantly receive AI-powered summaries, bullet-point insights, and extracted metadata. It saves time and cognitive load during legal reviews, research reading, or market analysis.
Static documents become interactive. Users can ask natural language questions and receive contextual answers from within the document, navigating complex reports conversationally.
Thanks to OpenAI’s streaming APIs and frameworks like Next.js 14, responses flow in real-time, boosting perceived performance and keeping the interaction smooth.
Even the best systems face interruptions. Production-grade RAG apps monitor connectivity and inform users gracefully if the chat fails or the connection is lost.
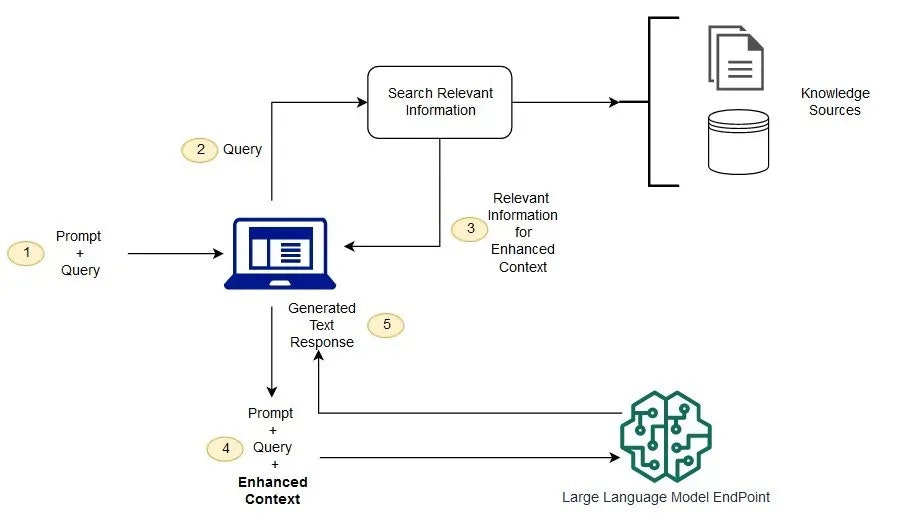
The application leverages Next.js 14 with the App Router, providing several architectural advantages:
The UI layer uses Tailwind CSS with a custom theme configuration supporting both light and dark modes. This approach ensures consistent styling while maintaining flexibility for future design iterations.

The heart of any RAG system lies in its document processing pipeline. Our implementation follows a sophisticated multi-stage approach:
When users upload PDFs, the system first extracts text content while preserving document structure. This involves:
We use semantic chunking strategies:
// Intelligent chunking strategy
function chunkDocument(text, options = {}) {
const {
maxChunkSize = 1000,
overlap = 200,
preserveStructure = true
} = options;
}
Effective chunking strategies include:
Each document chunk is converted to high-dimensional vector representations using OpenAI's embedding models. These embeddings capture semantic meaning, enabling similarity-based retrieval:
async function generateEmbeddings(chunks) {
const embeddings = await Promise.all(
chunks.map(chunk => openai.embeddings.create({
model: "text-embedding-3-small",
input: chunk.content
}))
);
return embeddings.map((embedding, index) => ({
...chunks[index],
embedding: embedding.data[0].embedding
}));
}
We store vectors in MongoDB Atlas with vector search enabled, alongside metadata.
The most technically challenging aspect of RAG systems is implementing efficient vector search. Our MongoDB-based approach includes several optimizations:

db.documents.createIndex({
"embedding": "vectorSearch"
}, {
"vectorSearchOptions": {
"type": "knn",
"dimensions": 1536,
"similarity": "cosine"
}
});
Vector queries are optimized for both accuracy and performance:
async function searchSimilarChunks(queryEmbedding, options = {}) {
const {
limit = 5,
threshold = 0.7,
filters = {}
} = options;
return await db.collection('documents').aggregate([
{
$vectorSearch: {
index: "vector_index",
path: "embedding",
queryVector: queryEmbedding,
numCandidates: limit * 10,
limit: limit,
filter: filters
}
},
{
$match: {
score: { $gte: threshold }
}
}
]);
}
Advanced RAG systems combine vector search with traditional text search for improved accuracy:

Production RAG applications require careful optimization across multiple dimensions:
Document processing can be memory-intensive, especially for large PDFs. Key optimizations include:
async function processDocumentInBatches(document, batchSize = 50) {
const chunks = chunkDocument(document);
const batches = [];
for (let i = 0; i < chunks.length; i += batchSize) {
const batch = chunks.slice(i, i + batchSize);
const embeddings = await generateEmbeddings(batch);
await storeBatch(embeddings);
// Prevent memory leaks
if (global.gc) global.gc();
}
}
Response streaming improves user experience significantly:
async function* streamRAGResponse(query, retrievedChunks) {
const completion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4",
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content: buildSystemPrompt(retrievedChunks)
},
{
role: "user",
content: query
}
],
stream: true
});
for await (const chunk of completion) {
if (chunk.choices[0]?.delta?.content) {
yield chunk.choices[0].delta.content;
}
}
}
Production RAG systems require comprehensive evaluation frameworks:
Extending beyond text to include images, tables, and other media types in document understanding and retrieval.
Integrating RAG with autonomous agents that can reason about when and how to retrieve information, potentially querying multiple knowledge bases.
Moving beyond general-purpose embedding models to domain-specific, fine-tuned retrievers that better understand specialized terminology and concepts.
Production RAG systems work best when architecture, speed, and user experience are designed together. Reliable retrieval, clear prompts, and stable pipelines matter more than model hype.
Start with one clear use case and measurable goals. Define quality targets, latency limits, and governance needs. Then improve continuously using user feedback and evaluation data.
Whether you are building a document assistant, support copilot, or research tool, these practices provide a strong baseline. They help your system stay accurate, fast, and maintainable as your content grows.

Software Engineer
Utkarsh is a mid-level Engineer with Strong experience in networking and server side technologies